Politics | Home / South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation
Last update: August, 14 2020
South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (SAARC)
| Type | |
| Regional Intergovernmental organisation | |
| Leaders | |
| Secretary-General | Esala Ruwan Weerakoon |
| Establishment | |
| 8 December 1985 | |
| Headquarters | |
| Kathmandu (Nepal) | |
| Population | |
| Population (2015) | 1,713,870,000 |
| Density of population | 336.1 P/km2 (870.5 P/sq mi) |
| Working language | |
| English | |
| Geography | |
| Area | 5,099,611 km2 (1,968,971 sq mi) |
| Economy | |
| GDP (PPP) (estimate 2017) | |
| Total | $11.64 trillion |
| GDP (nominal) (estimate 2017) | |
| Total | $3.31 trillion |
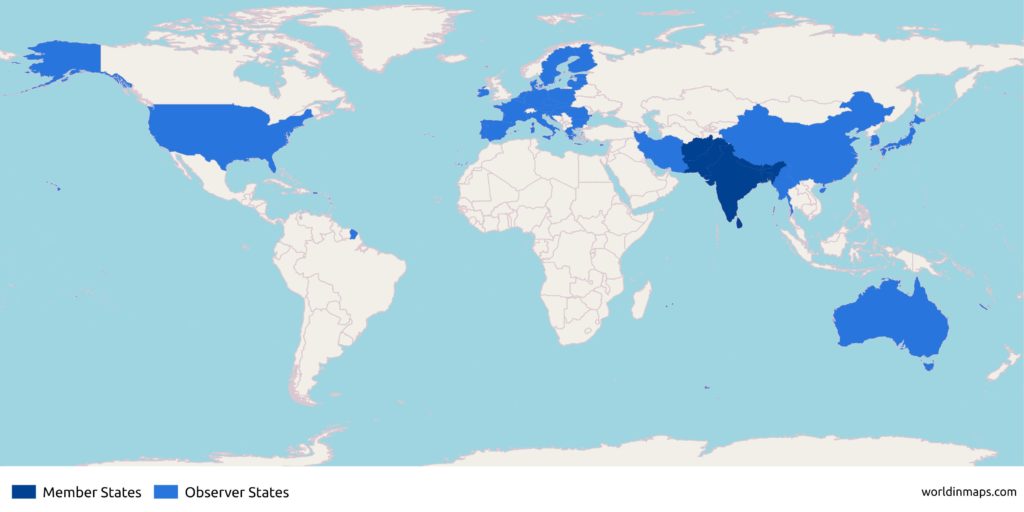
| Member States (8) | |
| Afghanistan | |
| Bangladesh | |
| Bhutan | |
| India | |
| Maldives | |
| Nepal | |
| Pakistan | |
| Sri Lanka | |
| Observer States (9) | |
| Australia | |
| China | |
| the European Union | |
| Iran | |
| Japan | |
| Mauritius | |
| Myanmar | |
| South Korea | |
| United States | |
| Website | |
| http://www.saarc-sec.org/ | |
Objectives of the South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (SAARC)
The South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (SAARC) is an economic and political organization of 8 countries in South Asia.
The main objectives of the SAARC are to promote economic growth, social progress and cultural development within the South Asia region. The objectives of the South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation as defined in its charter are:
- to promote the welfare of the peoples of SOUTH ASIA and to improve their quality of life
- to accelerate economic growth, social progress and cultural development in the region and to provide all individuals the opportunity to live in dignity and to realise their full potentials
- to promote and strengthen collective self-reliance among the countries of SOUTH ASIA
- to contribute to mutual trust, understanding and appreciation of one another’s problems
- to promote active collaboration and mutual assistance in the economic, social, cultural, technical and scientific fields
- to strengthen cooperation with other developing countries
- to strengthen cooperation among themselves in international forums on matters of common interests
- to cooperate with international and regional organisations with similar aims and purposes.
History
The South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation was initiated by the Bangladeshi president Ziaur Rahman. It was founded in New Delhi on 2 august 1983 and it was established by the signing of the SAARC Charter on 8 December 1985 in Dhaka.
At the creation, the SAARC had the following 8 member states:
During the 12th summits (2–6 January 2004), the member states have signed the South Asian Free Trade Area (SAFTA), which foresee the creation of a free trade area for an area covering 1.4 billion people.
In April 2007, Afghanistan joined the South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation.