History | Home / Cold war
Cold war maps
Table of contents
- Cold war – summary
- Cold war world maps and timeline
- End of the Second World War
- The Iron Curtain
- Civil war in Greece (1949)
- Civil war in China (1949)
- The Korean War (1950 – 1953)
- French Indochina war (1946 – 1954)
- The Warsaw Pact (1955)
- The Suez Canal crisis (1956)
- Sino-Soviet split (1956 – 1966)
- The non-Aligned Movement (1961)
- Cuban Missile Crisis (1962)
- Vietnam war (1955 – 1975)
- Expansion and the fall of the USSR
- Cold war maps of Europe
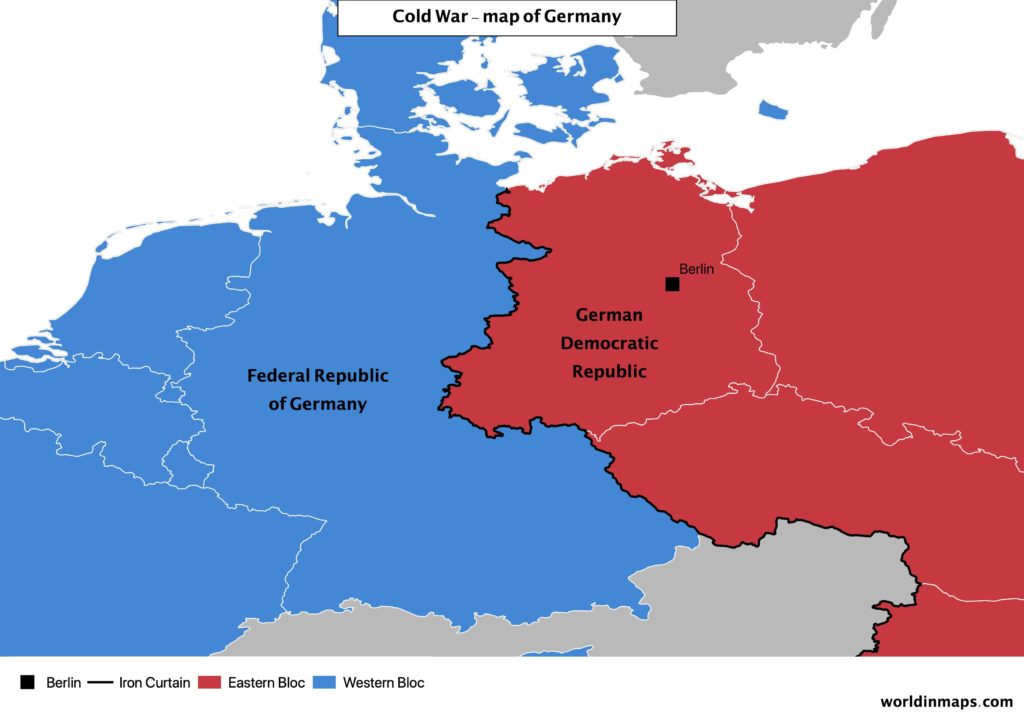
- Cold war map of Germany
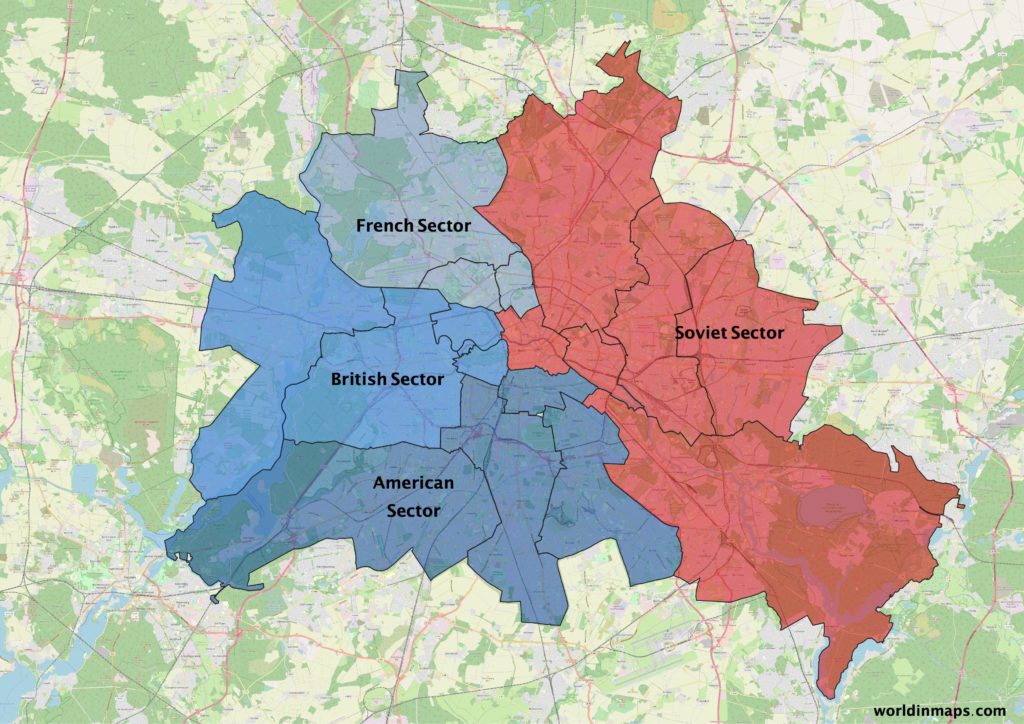
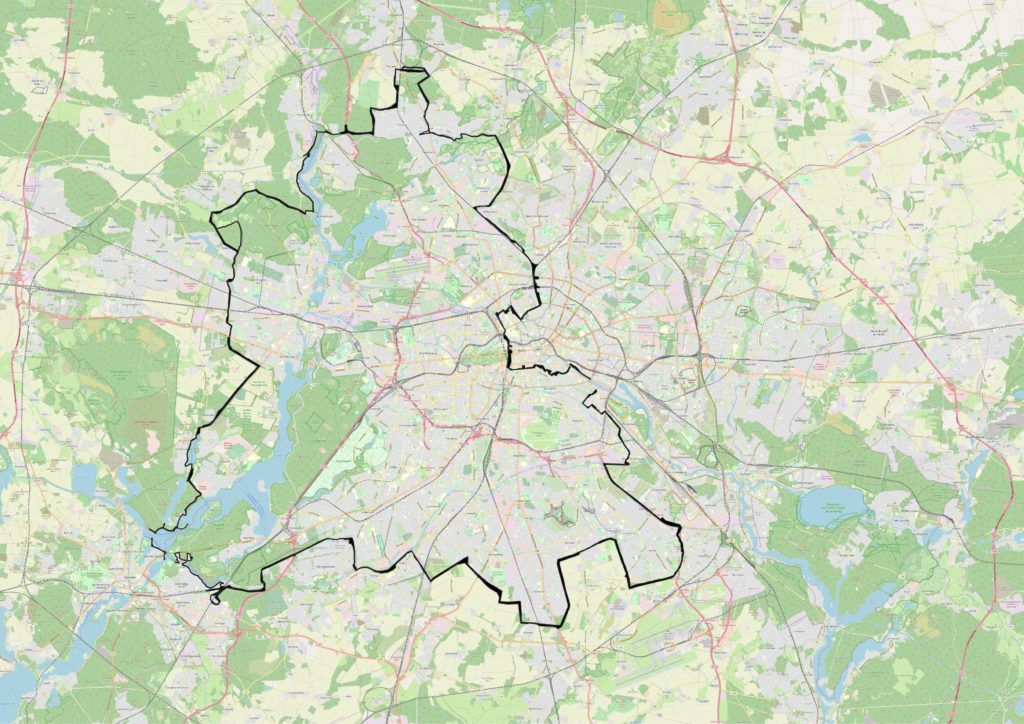
- Berlin cold war maps
- Cold war maps of Asia
- Recommended books
- Sources
Cold war – summary
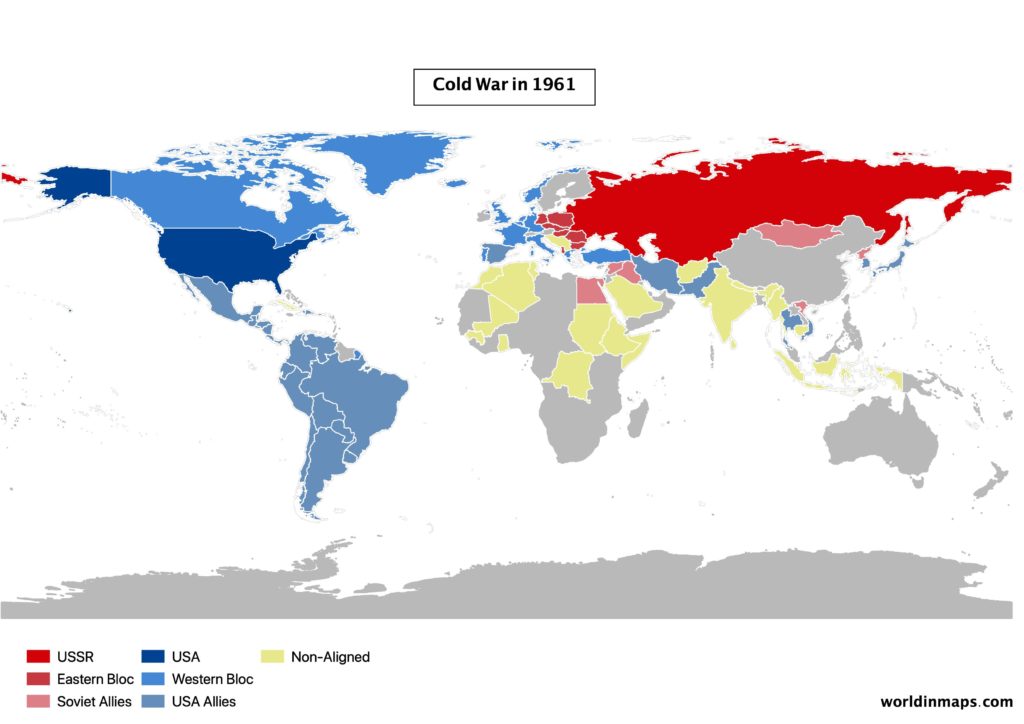
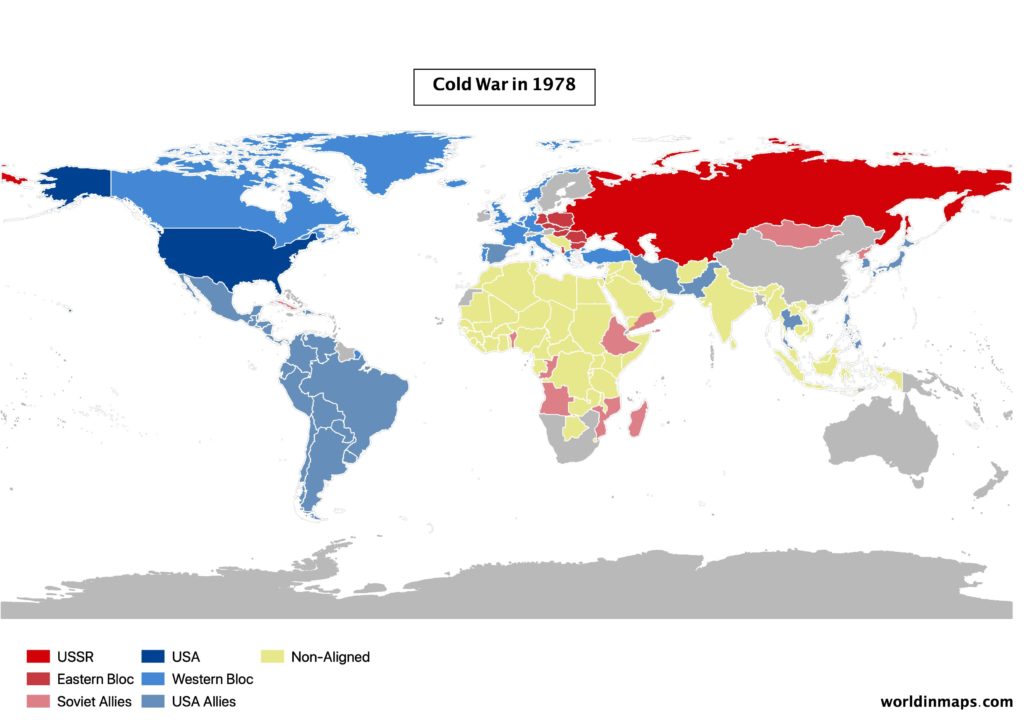
Different cold war maps will explain this period of strong geopolitical tensions between the USA and his allied (the Eastern Bloc) against the Soviet Union (Western Bloc). This period starts after the second world war, more precisely in 1947, and it finished in 1991 with the dissolution of the Soviet Union.
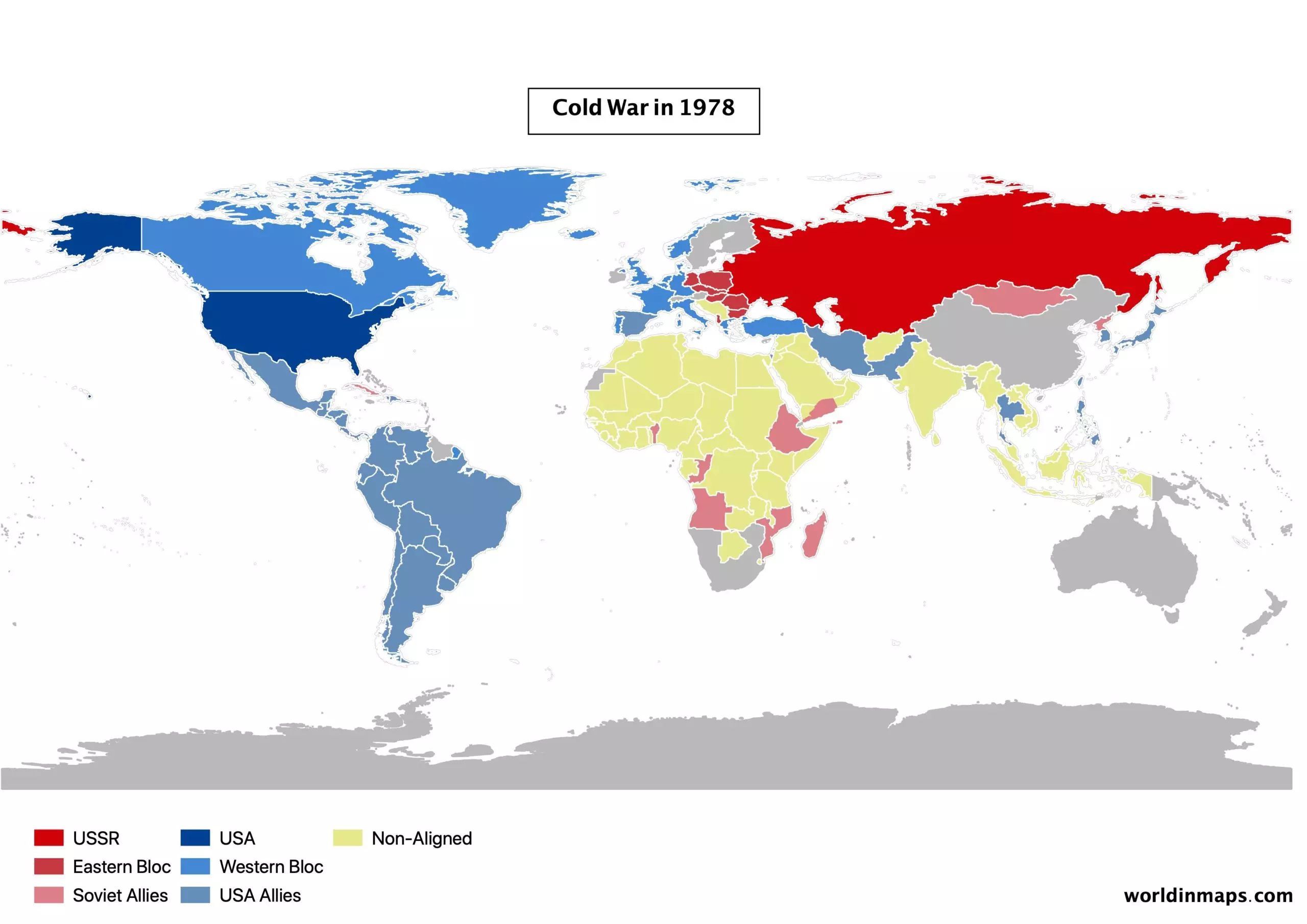
Cold war world maps and timeline
End of the Second World War
The Second World War left Major European countries weakened by years of War. USA and USSR (Union of Soviet Socialist Republics), that fought together to defeat the Nazi and the Empire of Japan, are therefore the 2 only remaining superpower at the end of the Second World War.
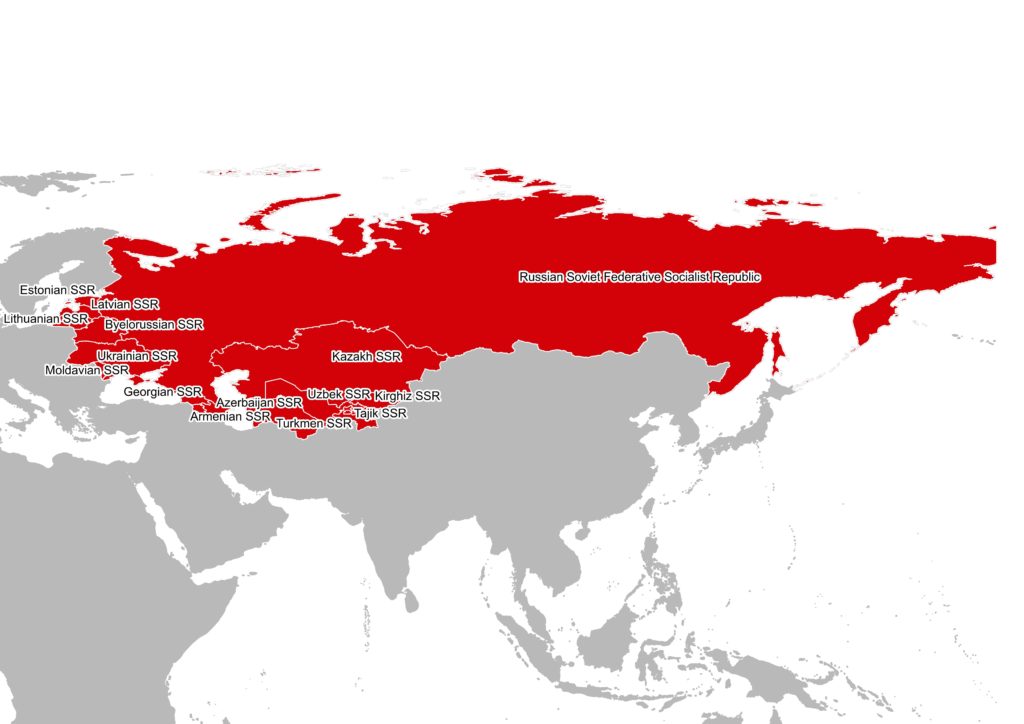
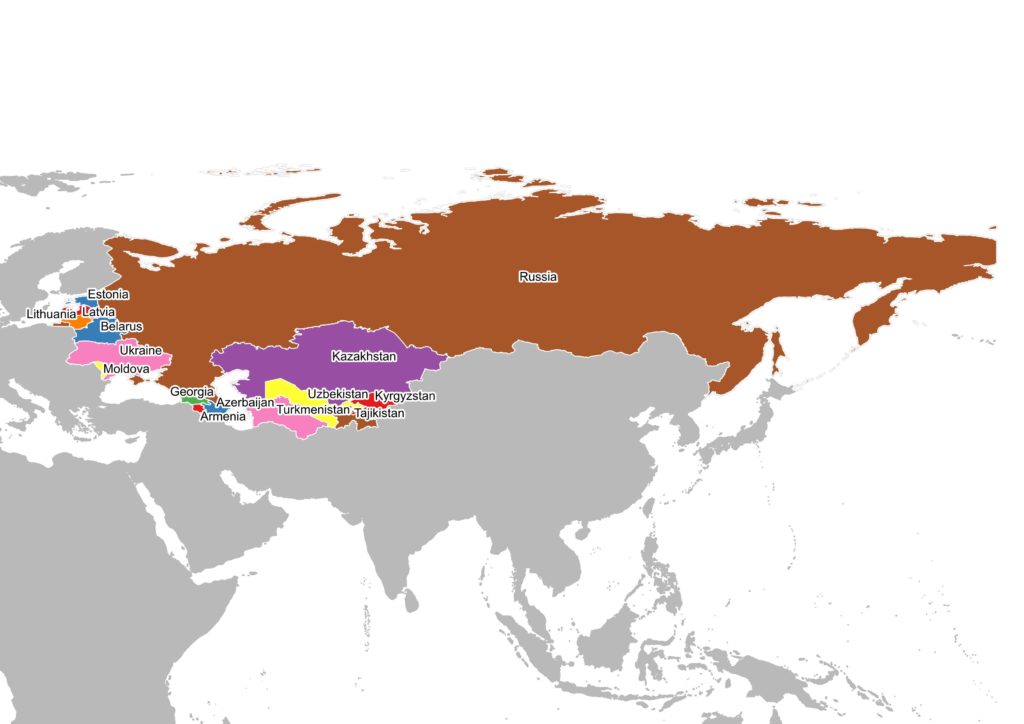
At that Period the USSR is a federal state of 15 republics headed by a single communist party.
These 15 republics were:
- Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic
- Estonian SSR
- Latvian SSR
- Lithuanian SSR
- Byelorussian SSR
- Ukrainian SSR
- Moldavian SSR
- Georgian SSR
- Armenian SSR
- Azerbaijan SSR
- Kazakh SSR
- Uzbek SSR
- Turkmen SSR
- Tajik SSR
- Kirghiz SSR
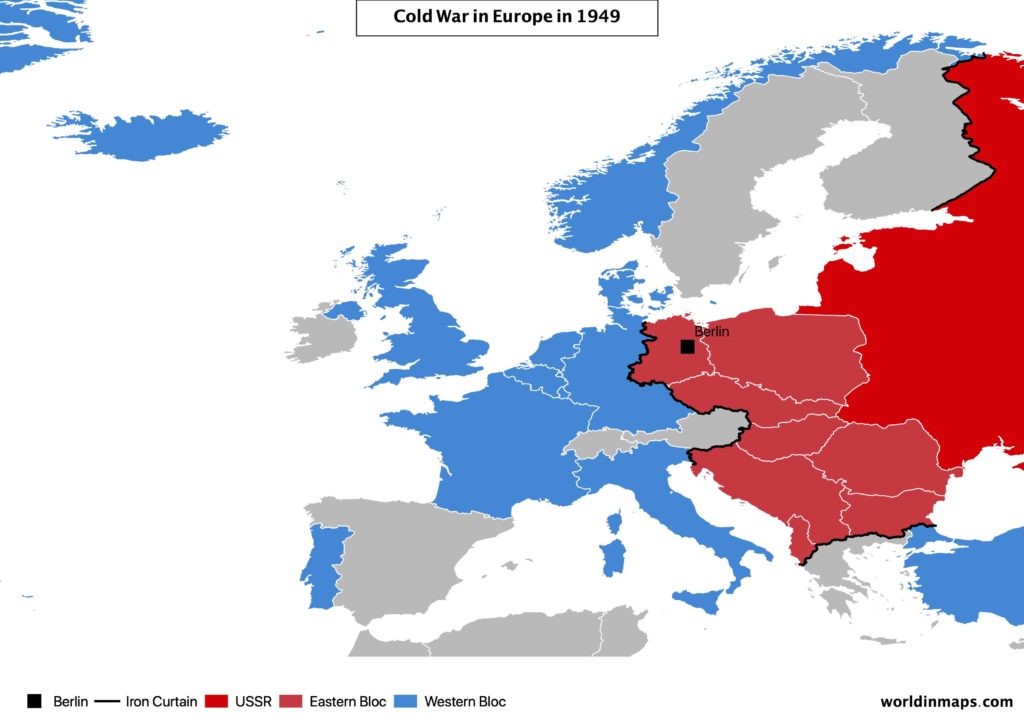
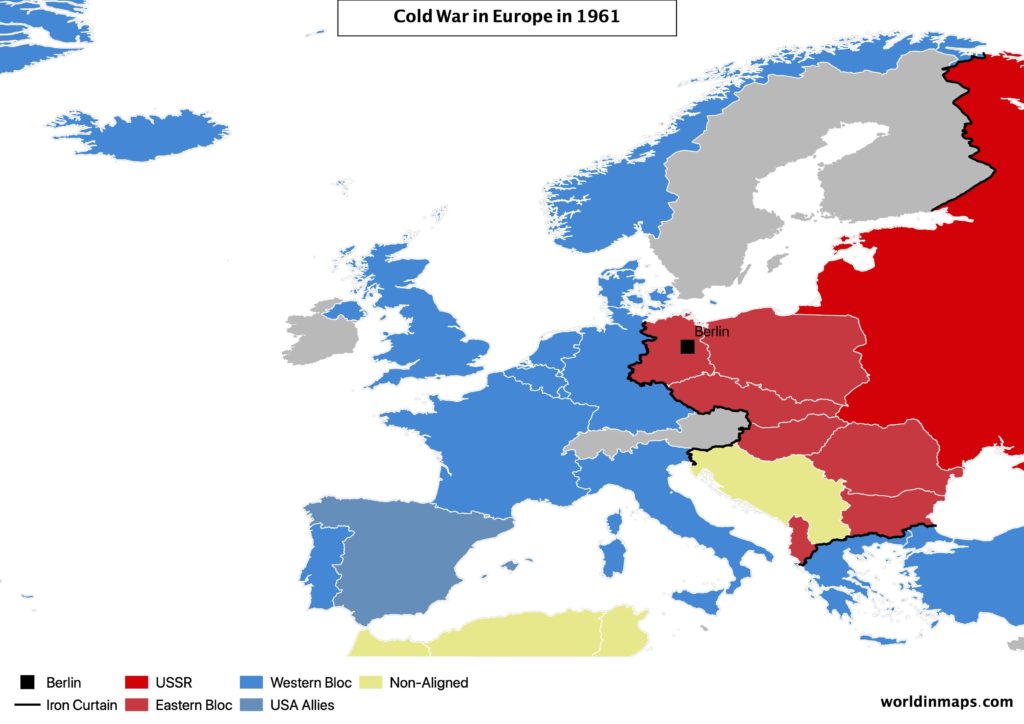
The Iron Curtain
So, after the Second World War the 2 superpowers (US and USSR) try to put their influence in Europe.
The US offer substantial loans to Europeans Countries (Austria, Belgium, Luxembourg, Denmark, France, West Germany, Greece, Iceland, Ireland, Italy, Trieste, Netherlands, Norway, Portugal, Sweden, Switzerland, Turkey and the United Kingdom), with the so called Marschall Plan, to rebuild their economy and establish trade links.
Meanwhile, the USSR, that wanted to protect his border, set up pro-Soviet countries in liberated countries (Poland, Czechoslovakia, Hungary, Yugoslavia, Romania, Bulgaria and Albania).
As a result, the Second World War left Europe divided into 2 parts, separated by what is called the Iron Curtain (from 1945 to 1991).
In 1949, the USA set up the NATO (North Atlantic Treaty Organization), which is an intergovernmental military alliance. The treaty was signed by the following European members: UK, France, Belgium, Netherlands, Luxembourg, Norway, Iceland, Portugal and Italie.
Throughout the cold war, there were many indirect conflicts between the two powers and their allies.
Civil war in Greece (1949)
It is the first indirect conflict. The Rebel Communist militia (supported by the Soviets and armed by Yugoslavia) enters into a civil war against the Monarchy (supported by the UK and then the USA). However, following to tensions, the USSR breaks its alliance with Yugoslavia. This weakens the Greeks communists who finally were forced to lay down their arms. As a result, Greece became part of the Western Bloc.
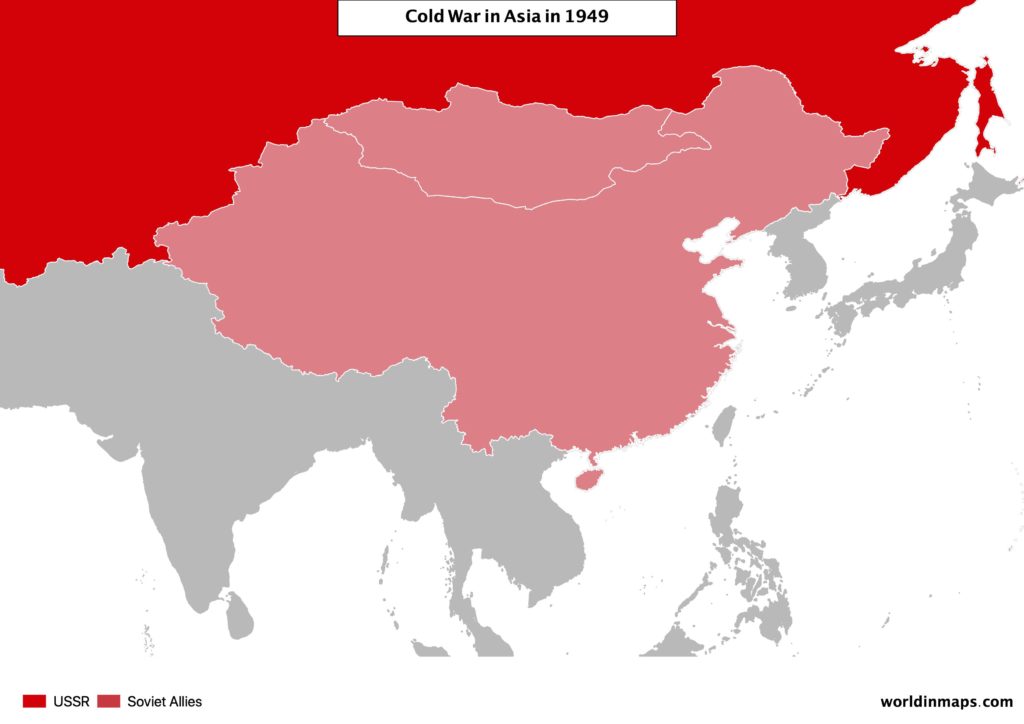
Civil war in China (1949)
After 3 years of civil war, the communists won against the nationalists, which retreat to Taiwan. With the winning of the communism in China, the USSR won an important Ally in the Region, who will therefore play a big role in the wars of Korea and French Indochina.
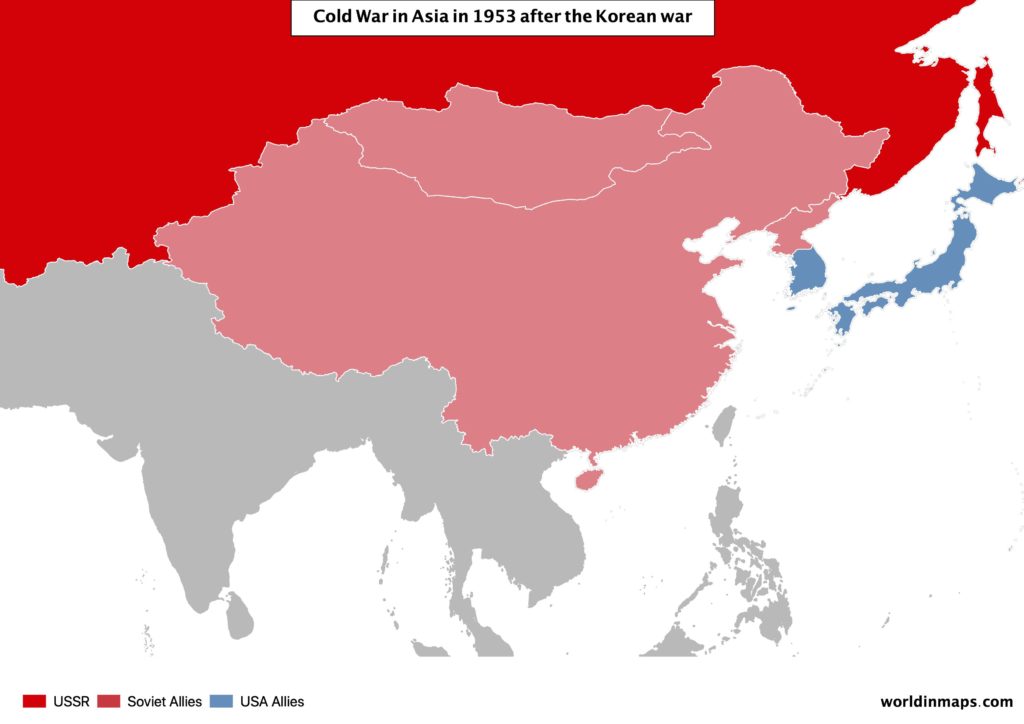
The Korean War (1950 – 1953)
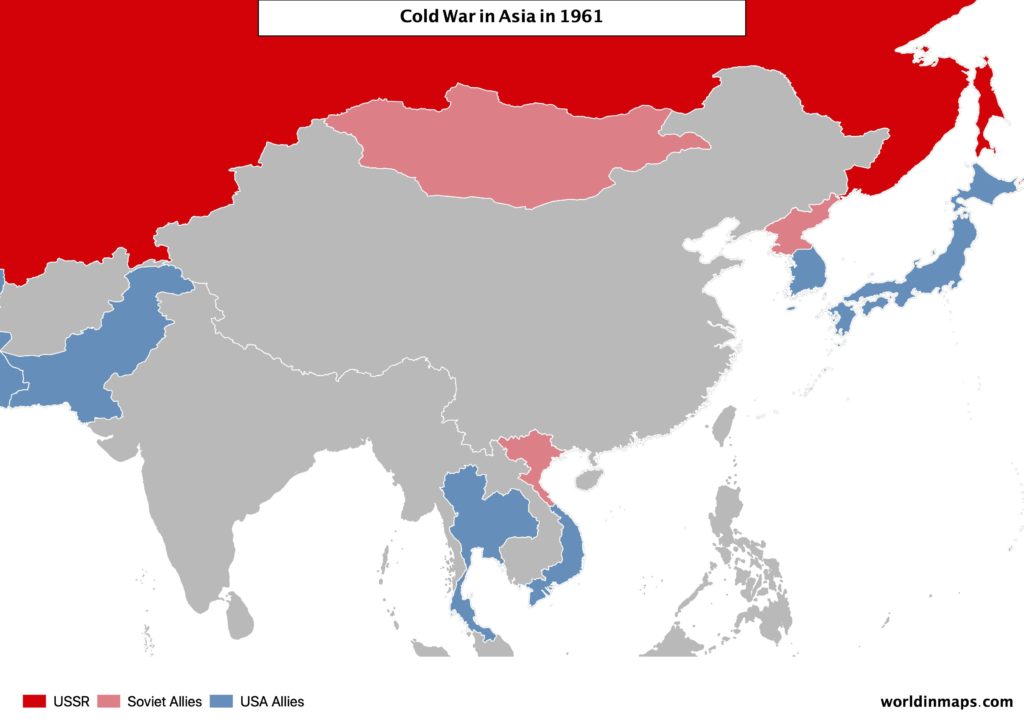
In short, this war was between the communist North Korea (with China on their sides) and the South Korea, which was supported by a United Nations-led International force directed by the USA. After 3 years of war, the ceasefire leaves Korea divided in 2.
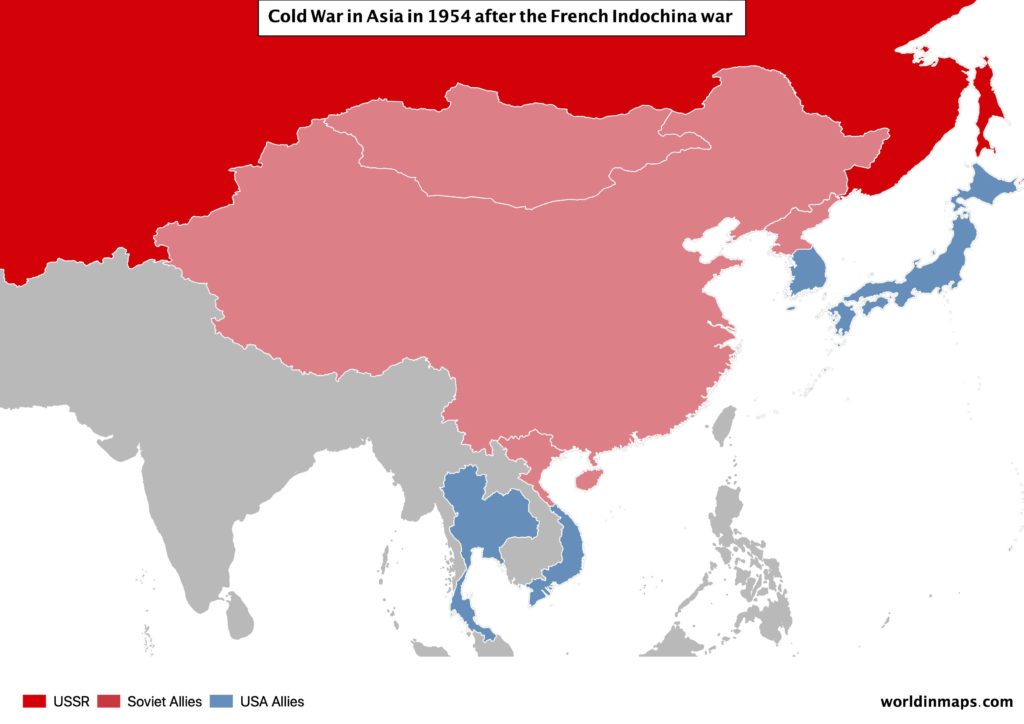
French Indochina war (1946 – 1954)
China intervenes also in this war by supporting the rebel Communists that were fighting against France, which struggle to regain control and finally had to leaves the region. French Indochina war leaves Vietnam divided in 2 parts. That is to say a north communist part and the nationalist south, supported by the USA. In addition, this marked the beginning of the Vietnam war.
The Warsaw Pact (1955)
In response to the NATO, the USSR creates its own military alliance (the Warsaw Pact). The countries that were part of this alliance are:
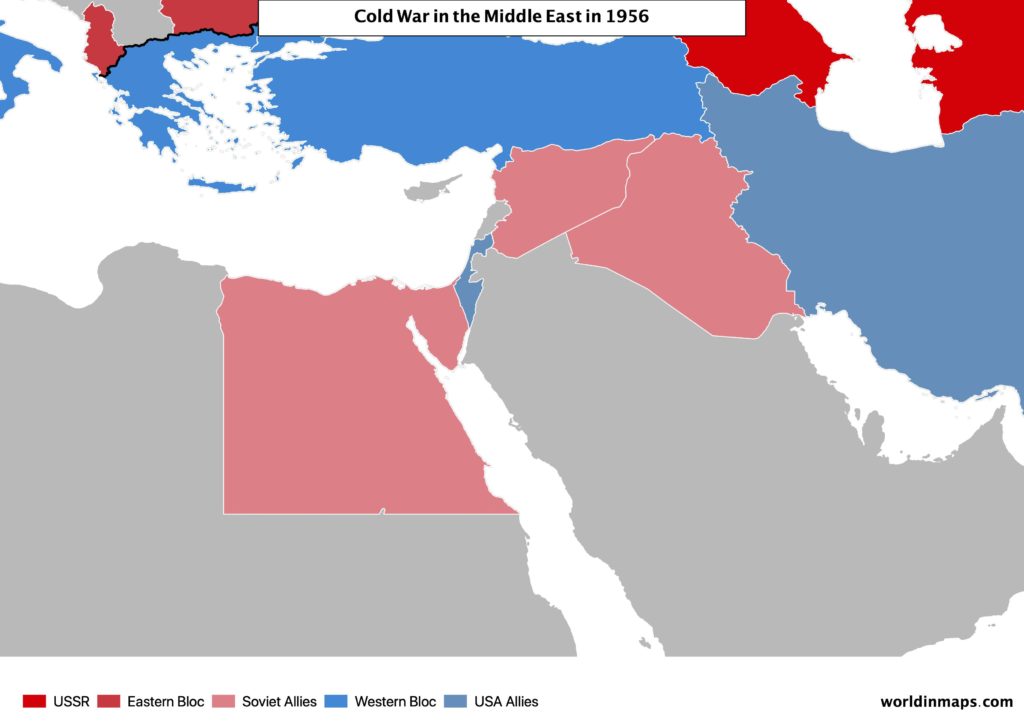
The Suez Canal crisis (1956)
Egypt was invaded by Israel and followed by the UK and France. The aims were to regain Western control of the Suez Canal. But USA and USSR quickly oppose to this attack and impose a ceasefire, which mark the end of the European dominance in the region. As a result, the USSR took benefit of it.
Sino-Soviet split (1956 – 1966)
Because of disagreements, China breaks its alliance with the USSR and become a new world power.
The non-Aligned Movement (1961)
Many countries breaks with the 2 main camps and decided to remain neutral.
Cuban Missile Crisis (1962)
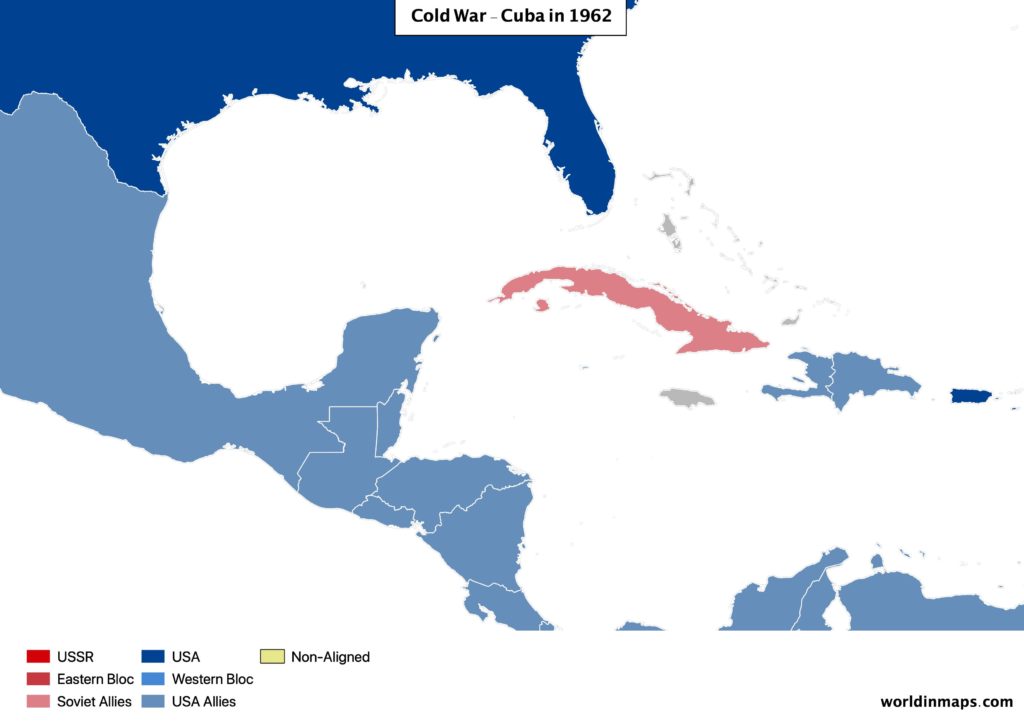
In South America, USA ensure to let no room for Communism, but it fails in Cuba to avoid the communism to outbreak in that country. On the other hand, USSR took advantage of it to send soldiers, military ships and missiles are installed to point to the USA. The tension was so high that marine force of both sides were ready to face off. Most importantly many countries were preparing for a World War III. But after negotiating USSR agreed to remove his military facilities. In return USA will not attack Cuba and will retrieve their missiles from Europe.
Vietnam war (1955 – 1975)
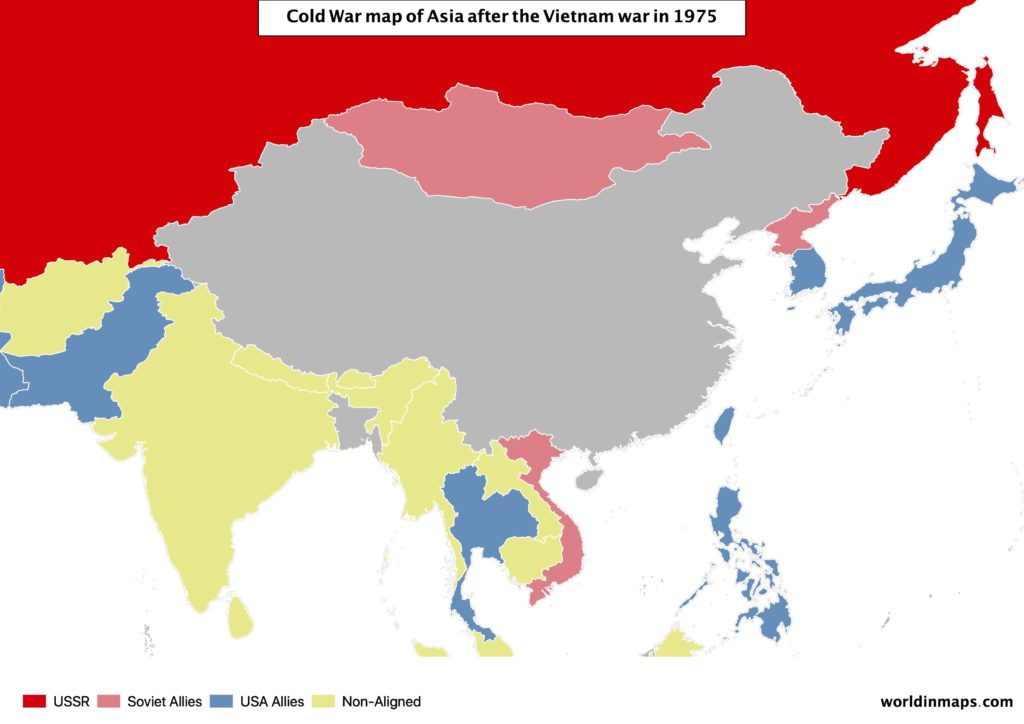
The start of the Vietnam war found its root in the French Indochina war, because it left a communist north part and a nationalist south part. The south was supported by the USA. The US intervention in Vietnam is usually set to 1961, but it is since 1965 that US start to be military massively involved in this war. However, this decision was against the point of view of France, that wanted a peaceful solution, and this bring France to quit the NATO in 1966. The Vietnam war took end in 1975 with the winning of the communists and the heavy defeat of the US. As a result, this had weakened the image of the US.
Expansion and the fall of the USSR
Taking profit of the US defeat in Vietnam, the USSR took after that the opportunity to expand its political influence in the World by supporting African Communist militias who took the power in newly independent countries.
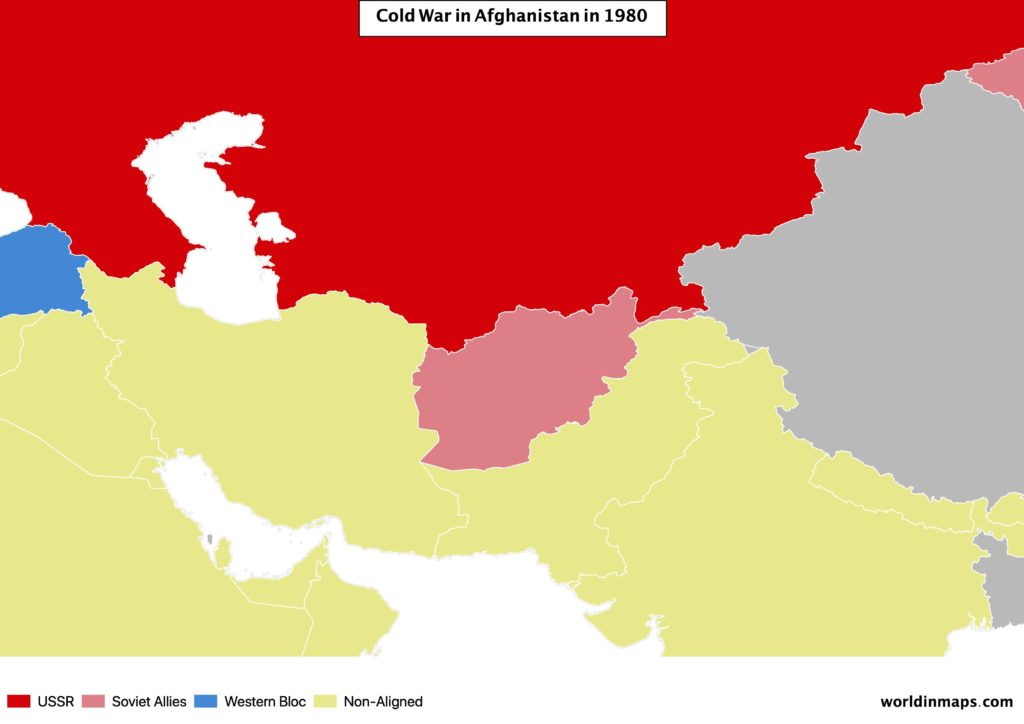
And it also support communist regime that fight in Afghanistan against a group of Islamist supported and funded by several countries, under which the US.
The USSR also replaces its missiles that point to Europe with new missiles. As a result, this started the Euromissile crisis, which pushes US to install new of its missiles in Europe. But this run for military armaments bring the USSR to run out of money and started to make reforms. The 2 superpowers finally meet to begin disarmament negotiations in 1988. USSR retreat from Afghanistan and stop funding communist militias in Africa. In 1989, the Soviet Union cannot face numerous revolts, the Berlin wall is destroyed and Germany is reunited. In 1991, USSR implode and the 15 republics become independent states, marking therefore the end of the cold war.
The 15 new states are:
- Russia
- Estonia
- Latvia
- Lithuania
- Belarus
- Ukraine
- Moldova
- Georgia
- Azerbaijan
- Armenia
- Kazakhstan
- Uzbekistan
- Kyrgyzstan
- Turkmenistan
- Tajikistan
Cold war maps of Europe
Cold war map of Germany
Berlin cold war maps
Cold war maps of Asia
Recommended books