Politics | Home / Commonwealth
Last update: July, 5 2020
Commonwealth of Nations

| Type | |
| Intergovernmental organisation | |
| Leaders | |
| Head | Queen Elizabeth II |
| Secretary-General | Patricia Scotland |
| Chair-in-Office | Boris Johnson |
| Establishment | |
| Balfour Declaration | 19 November 1926 |
| Statute of Westminster | 11 December 1931 |
| London Declaration | 28 April 1949 |
| Headquarters | |
| Marlborough House London, SW1 United Kingdom | |
| Population | |
| Population (2016) | 2,418,964,000 |
| Density of population | 75 P/km2 |
| Working language | |
| English | |
| Geography | |
| Area | 29,958,050 km2 |
| Member States (54) | |
| Antigua and Barbuda | |
| Australia | |
| The Bahamas | |
| Bangladesh | |
| Barbados | |
| Belize | |
| Botswana | |
| Brunei | |
| Cameroon | |
| Canada | |
| Cyprus | |
| Dominica | |
| Eswatini | |
| Fiji | |
| The Gambia | |
| Ghana | |
| Grenada | |
| Guyana | |
| India | |
| Jamaica | |
| Kenya | |
| Kiribati | |
| Lesotho | |
| Malawi | |
| Malaysia | |
| Maldives | |
| Malta | |
| Mauritius | |
| Mozambique | |
| Namibia | |
| Nauru | |
| New Zealand | |
| Nigeria | |
| Pakistan | |
| Papua New Guinea | |
| Rwanda | |
| Saint Kitts and Nevis | |
| Saint Lucia | |
| Saint Vincent and the Grenadines | |
| Samoa | |
| Seychelles | |
| Sierra Leone | |
| Singapore | |
| Solomon Islands | |
| South Africa | |
| Sri Lanka | |
| Tanzania | |
| Tonga | |
| Trinidad and Tobago | |
| Tuvalu | |
| Uganda | |
| United Kingdom | |
| Vanuatu | |
| Zambia | |
| Website | |
| thecommonwealth.org | |
Meaning of the Commonwealth
The Commonwealth of Nations (or Commonwealth) is a political association of 54 member states that shares goals like development, democracy and peace. Nearly all members are former territories of the British Empire.
It dates from the first half of the 20th century with decolonisation of the British Empire through increased self-governance and it was originally created as the British Commonwealth of Nations. Today any country can join the Commonwealth.
The Commonwealth have 2.4 billion people and includes both advanced economies and developing countries. 32 of the 54 members are small states (including many island nations).
It is not to be confused with:
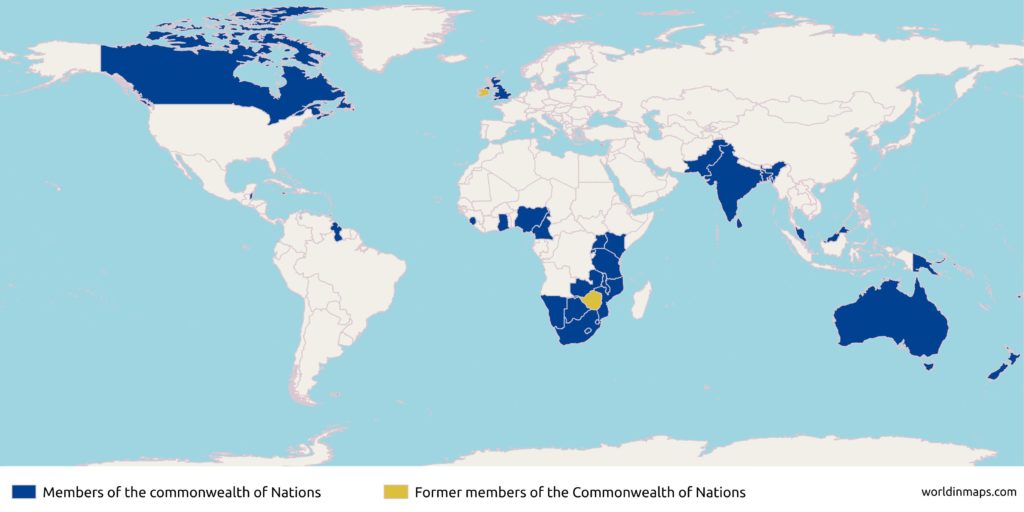
World map with the countries of the Commonwealth of Nations
Former members of the Commonwealth of Nations
- Republic of Ireland: 19 November 1926 – 18 April 1949
- Zimbabwe: 1 October 1980 – 7 December 2003